FinanceOS erp software examples
How do ERP systems support compliance and risk management in FinanceOS activities?
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems play a crucial role in supporting compliance and risk management in Financial Planning & Analysis (FinanceOS) activities by integrating various financial processes and data into a single system. This consolidation enables organizations to ensure accuracy, consistency, and real-time visibility into financial operations, which are essential for adhering to regulatory requirements and managing risks. ERP systems automate financial reporting processes, reducing the risk of human error and ensuring that reports are generated in accordance with the latest accounting standards and regulations. They also provide audit trails, which are critical for compliance purposes, as they offer transparent insight into financial transactions and enable easy tracking of data for audits. Furthermore, ERP systems can enforce internal controls and compliance policies by setting permissions and roles, ensuring that only authorized personnel can access sensitive financial information, thereby enhancing data security and regulatory compliance.
example:
an organization subject to the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) can leverage its ERP system to automate the enforcement of internal controls and documentation required by the act. The ERP system can be configured to require dual approvals for financial transactions, ensuring that no single individual has unchecked control over financial processes, thus mitigating the risk of fraud. Additionally, the system can automatically generate the necessary reports for SOX compliance, such as balance sheets and cash flow statements, with the required level of detail and within the stipulated timelines. This automation not only streamlines the compliance process but also significantly reduces the risk of non-compliance penalties and enhances the organization’s ability to manage financial risks more effectively.
the role of ERP in aligning FinanceOS functions with overall business strategy
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems play a crucial role in aligning Financial Planning & Analysis (FinanceOS) functions with the overall business strategy by providing a unified platform that integrates various business processes and data streams. This integration facilitates real-time visibility and access to financial and operational data, enabling FinanceOS teams to generate more accurate forecasts, budgets, and financial analyses. With ERP systems, organizations can streamline their FinanceOS processes, reducing manual data entry and errors, and improving efficiency. By aligning financial planning with strategic objectives, companies can make informed decisions, allocate resources more effectively, and adapt quickly to market changes or operational challenges. ERP systems help in bridging the gap between financial planning and strategic goals by ensuring that financial decisions are based on comprehensive, up-to-date information, aligning financial objectives with the company’s long-term vision.
example:
a manufacturing company implementing an ERP system can integrate its sales, production, and financial planning processes. This integration allows the FinanceOS team to directly link sales forecasts with production planning and financial budgets. If the sales forecasts indicate an increase in demand for certain products, the ERP system can automatically adjust production schedules and financial budgets to align with these forecasts. This ensures that the company’s financial planning is directly supporting its strategic goal of meeting market demand efficiently. The ERP system enables the company to dynamically adjust its operations and financial planning in response to market trends, improving responsiveness and competitive advantage. This example illustrates how ERP systems facilitate the alignment of FinanceOS functions with overall business strategy, enabling organizations to operate more strategically and effectively.
What future ERP innovations will shape FinanceOS practices?
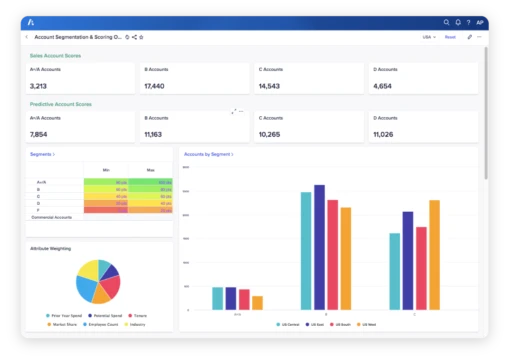
Future innovations in Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are expected to significantly influence Financial Planning & Analysis (FinanceOS) practices by integrating advanced technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and real-time data analytics. These innovations aim to enhance accuracy, efficiency, and strategic insights within financial operations. For instance, AI and ML can automate routine FinanceOS tasks such as data collection and analysis, enabling finance teams to focus on more strategic activities like forecasting and decision support. Additionally, the integration of real-time data analytics into ERP systems will allow FinanceOS professionals to access up-to-the-minute financial data, improving the timeliness and relevance of financial reports and forecasts. This can lead to more informed decision-making and a more agile response to market changes.
example:
An example of such innovation is the development of predictive analytics within ERP systems, which can transform FinanceOS practices by providing forward-looking insights based on historical data trends and patterns. For instance, an ERP system equipped with predictive analytics could analyze past sales data, market trends, and economic indicators to forecast future revenue streams and identify potential financial risks before they materialize. This capability would enable FinanceOS teams to proactively manage financial performance, optimize resource allocation, and refine their strategic planning processes, thereby enhancing the overall competitiveness and financial health of the organization.
How does ERP facilitate real-time financial reporting and analysis for FinanceOS?
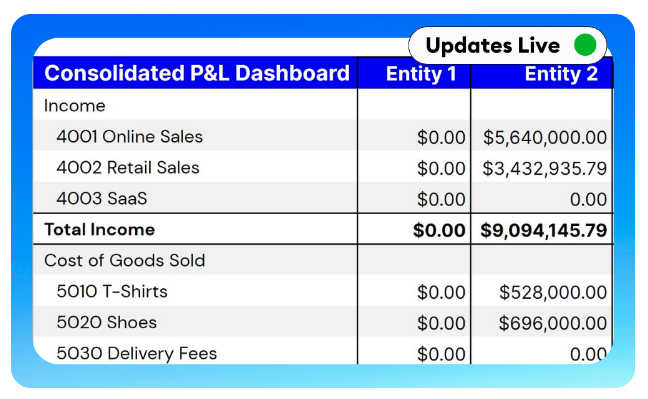
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems play a crucial role in enhancing real-time financial reporting and analysis for Financial Planning & Analysis (FinanceOS) by integrating various financial processes within an organization. This integration allows for the seamless flow of financial data across departments, eliminating data silos and ensuring that financial information is up-to-date and accessible. ERP systems automate many routine financial tasks, such as transaction recording, account reconciliation, and financial statement preparation. This automation reduces the time and effort required for data compilation and increases the accuracy of financial reports. Additionally, ERPs offer advanced analytics and reporting tools that enable FinanceOS professionals to perform in-depth financial analysis, forecast future trends, and make data-driven decisions. These tools often include dashboards and visualization capabilities, making it easier to interpret complex financial data in real time.
example:
consider a manufacturing company that implements an ERP system to streamline its financial operations. Before the ERP implementation, the company relied on manual processes and separate software solutions for accounting, inventory management, and sales, which often resulted in outdated and inconsistent financial data. After adopting an ERP system, the company can automatically capture and consolidate financial data from all departments in real time. This integration allows the FinanceOS team to quickly generate accurate financial reports, such as profit and loss statements and balance sheets, without the need for manual data consolidation. Moreover, the ERP system enables the FinanceOS team to conduct real-time analysis of financial performance against budgets and forecasts, identify variances, and take corrective actions promptly, thereby improving financial planning and decision-making processes.
Can ERP customization significantly impact FinanceOS efficiency and outcomes?
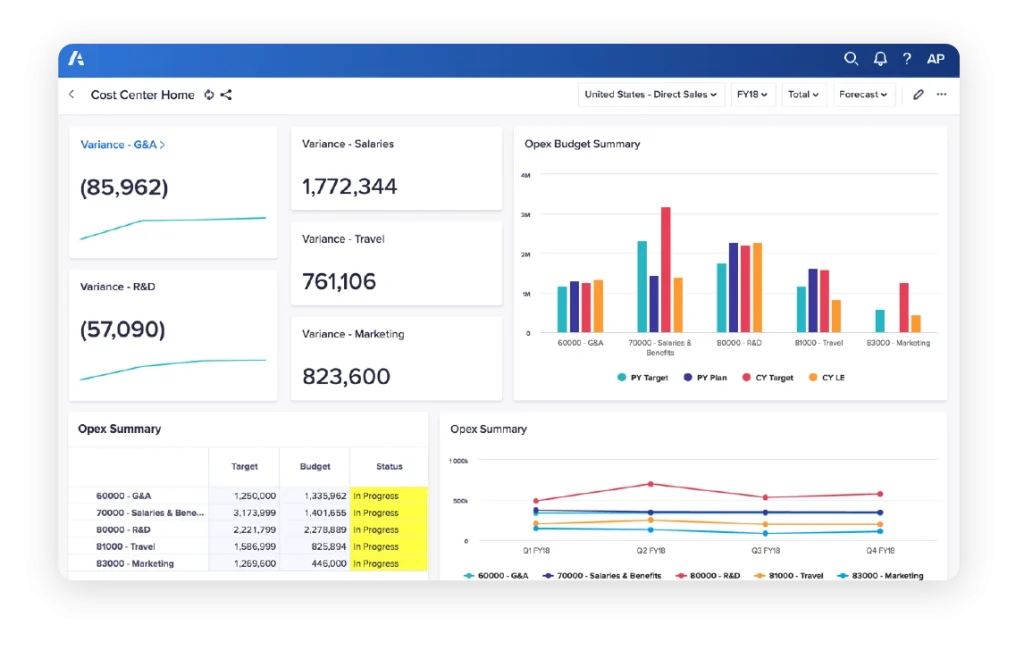
Yes, ERP customization can significantly impact Financial Planning & Analysis (FinanceOS) efficiency and outcomes. By tailoring an ERP system to the specific needs and processes of a business, companies can streamline data collection, improve accuracy, and enhance analysis capabilities. Custom ERP solutions enable more efficient data integration from various sources, reducing manual data entry and the potential for errors. This streamlined data flow allows FinanceOS teams to access real-time financial data, leading to quicker and more informed decision-making processes. For instance, customized dashboards and reporting tools within an ERP can provide immediate insights into financial performance, cash flow, and budget variances, enabling analysts to identify trends and make strategic adjustments more rapidly.
example:
An example of ERP customization impacting FinanceOS efficiency can be seen in a manufacturing company that integrates its ERP system with its production and supply chain management tools. By customizing the ERP to automatically pull in real-time production data and correlate it with financial metrics, the company can accurately forecast production costs, manage budgets more effectively, and optimize inventory levels based on financial insights. This level of integration and customization helps the company to not only reduce costs but also to improve its agility in responding to market changes, thereby enhancing overall financial performance and strategic planning. Through such customizations, ERP systems become not just tools for recording financial transactions but strategic platforms for advanced financial analysis and decision-making.
What cost-benefit considerations should guide ERP selection for FinanceOS functions?
When selecting an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system for Financial Planning & Analysis (FinanceOS) functions, several cost-benefit considerations are paramount. Initially, the cost of acquisition, implementation, and ongoing maintenance must be weighed against the expected benefits in terms of efficiency gains, accuracy improvements, and decision-making support. An ERP system that integrates seamlessly with existing financial processes can reduce manual data entry, minimize errors, and provide real-time financial insights, thereby enhancing strategic planning and forecasting capabilities. However, the costs are not limited to financial outlays but also include the time and resources required for training staff and adapting business processes to the new system. Thus, the chosen ERP should offer a user-friendly interface, customizable reporting features, and scalability to grow with the organization’s needs.
example:
consider a manufacturing company implementing an ERP system to improve its FinanceOS functions. The selected ERP system might come with a significant upfront cost, including software licensing, hardware upgrades, and consultant fees for customization and training. However, the benefits could include streamlined inventory management, more accurate cost tracking, and integrated budgeting and forecasting tools, leading to better capital allocation and reduced operational costs. If the ERP enables the company to reduce inventory overstock by 20% and shorten the budgeting cycle by 30%, these tangible improvements can quickly offset the initial investment. This scenario underscores the importance of evaluating ERP options not just on their direct costs but on their potential to drive financial performance improvements over time.
In Conclusion
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are vital in enhancing compliance and risk management within Financial Planning & Analysis (FinanceOS) activities by centralizing financial processes and data. This centralization ensures accuracy, consistency, and real-time insight into financial operations, crucial for meeting regulatory requirements and managing risks effectively. Through automation, ERP systems minimize human error in financial reporting, align reports with current accounting standards, and maintain audit trails for compliance verification. They further bolster compliance by enforcing internal controls and managing access to sensitive financial information, thereby securing data and adhering to regulations. For example, in adherence to the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, ERP systems can automate internal controls and documentation, require dual approvals for financial transactions to prevent fraud, and generate necessary reports, streamlining compliance processes and mitigating non-compliance risks.
Additionally, ERP systems play a pivotal role in aligning FinanceOS functions with overall business strategies by offering a unified platform that integrates business processes and data, facilitating accurate financial forecasting, budgeting, and analysis. This alignment enables informed decision-making, effective resource allocation, and rapid adaptation to market or operational changes, ensuring financial objectives are in sync with long-term business goals. Innovations in ERP, such as AI, ML, and real-time data analytics, are poised to further revolutionize FinanceOS practices by automating routine tasks and providing predictive insights for proactive financial management. Customization of ERP systems to specific business needs enhances efficiency and strategic decision-making, while cost-benefit considerations in ERP selection are crucial for ensuring that the benefits in operational efficiency, decision support, and strategic planning outweigh the costs of implementation and maintenance, ultimately driving financial performance improvements.